在做灰盒测试和恶意程序分析的时候,经常需要寻找创建、删除、修改的文件,而在无法确定操作的文件或生成的文件路径时,就需要用到可以监控文件和目录的工具了。比如测试任意文件上传时,文件名被改为随机字符串且HTTP响应中不返回文件路径;通过写文件的payload批量测试无回显命令注入漏洞;测试缓冲区溢出漏洞或拒绝服务漏洞时,可能会生成一些dump文件;这些测试场景下使用文件监控工具总比一直手动执行ls命令要好吧。
简介
inotify-tools是用C编写的,除了要求内核支持inotify外,不依赖于其他库。它提供了一套C开发接口库函数,使得开发者可以在自己的应用程序中集成文件系统监控功能。这些工具可以通过命令行或脚本使用,提供了灵活的监控选项和输出格式。inotify-tools 主要提供了两个命令行工具:inotifywait 和 inotifywatch。
inotifywait的功能
- 用于监控文件或目录的变化,如访问、写入、修改、删除等。
- 可以实时监控指定目录或文件系统的所有事件。
- 支持递归监控,即监控整个目录树的变化。
- 可以指定监控特定类型的事件,如创建、删除、修改等。
- 可以设置超时时间,如果在指定时间内没有事件发生,则退出。
- 可以持续监控,直到手动停止或发生特定事件后退出。
- 可以将监控结果输出到标准输出、文件或syslog。
inotifywatch的功能
- 用于统计文件系统访问的次数和类型。
- 可以收集关于被监视的文件系统的统计数据,如每个inotify事件发生的次数。
- 适合用于分析文件系统的使用情况。
GitHub地址:https://github.com/inotify-tools/inotify-tools
安装
可以使用包管理器或通过源码安装。
包管理器安装
Debian/Ubuntu
sudo apt-get install inotify-toolsCentos
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum install inotify-tools源码安装
- 克隆仓库到本地机器:
git clone https://github.com/inotify-tools/inotify-tools.git - 进入仓库目录:
cd inotify-tools - 自动创建config脚本:
./autogen.sh - 配置构建系统:
./configure - 编译源代码:
make - 安装库和头文件到系统路径(可能需要 sudo):
sudo make install
或者直接执行:./build_and_test.sh
使用教程
notifywait 基本用法
inotifywait 命令用于等待文件系统上的特定事件。以下是一些常用的选项:
-m或--monitor:持续监控,而不是在第一个事件发生后就退出。-r或--recursive:递归监控,监视指定目录及其所有子目录。-e或--event:指定要监控的事件类型,如create、delete、modify、access等。-t或--timeout:设置超时时间,单位为秒。
使用示例:inotifywait -m -r -e create,modify /root
这个命令会递归监控 /root 目录,输出所有创建和修改事件,并持续监控。
inotifywatch 基本用法
inotifywatch 命令用于收集和显示文件系统事件的统计信息。以下是一些常用的选项:
-r或--recursive:递归监控指定目录及其所有子目录。-e或--event:指定要监控的事件类型。
使用示例:inotifywatch -r -e create,modify /root
这个命令会递归监控 /root 目录,并显示所有创建和修改事件的统计信息。
FAQ
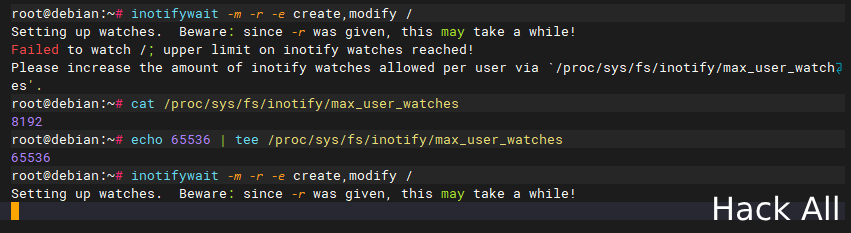
直接监控根目录时,超出了系统允许的每个用户可以监视的 inotify 事件的数量上限,会发生错误:
Failed to watch /; upper limit on inotify watches reached!Please increase the amount of inotify watches allowed per user via `/proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches'.要解决这个问题,需要增加每个用户允许的 inotify 监视器的数量:
- 查看当前的限制:
cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches - 增加限制(例如,增加到65536):
echo 65536 | sudo tee /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
作为C库使用
inotify-tools安装成功后,系统存在/usr/local/include/inotifytools/inotifytools.h文件,根据inotifytools.h头文件内容,inotifytools 库提供了一套丰富的函数来处理 inotify 事件。这些函数包括但不限于:
- 字符串和事件相互转换的函数,如
inotifytools_str_to_event和inotifytools_event_to_str。 - 设置和获取监视的文件名,如
inotifytools_set_filename_by_wd和inotifytools_filename_from_watch。 - 监视文件和目录的函数,如
inotifytools_watch_file和inotifytools_watch_recursively。 - 处理 inotify 事件的函数,如
inotifytools_next_event和inotifytools_next_events。 - 错误处理和统计信息获取的函数,如
inotifytools_error和inotifytools_get_stat_by_wd。 - 格式化输出 inotify 事件的函数,如
inotifytools_printf和inotifytools_snprintf。
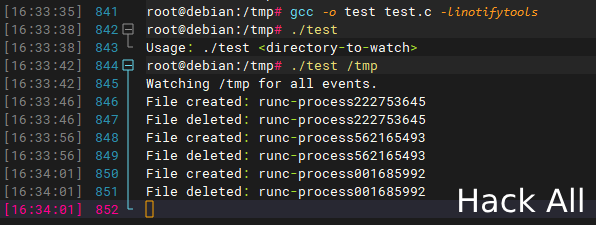
示例代码:test.c
#include <inotifytools/inotifytools.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/inotify.h> // 确保包含标准的 inotify 头文件
#ifndef IN_ALL_EVENTS
#define IN_ALL_EVENTS (IN_CREATE | IN_DELETE | IN_MODIFY | IN_MOVED_FROM | IN_MOVED_TO)
#endif
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <directory-to-watch>\n", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
const char *directory_to_watch = argv[1];
int fd;
// 初始化 inotify
if (inotifytools_init(0, 0, 0) < 0) {
perror("inotifytools_init");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 递归监视目录
int wd = inotifytools_watch_recursively(directory_to_watch, IN_ALL_EVENTS);
if (wd < 0) {
perror("inotifytools_watch_recursively");
inotifytools_cleanup();
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Watching %s for all events.\n", directory_to_watch);
while (1) {
// 获取下一个事件
struct inotify_event *event = inotifytools_next_event(-1);
if (event == NULL) {
if (inotifytools_error() != 0) {
perror("Error occurred while waiting for events");
}
break;
}
// 处理事件
if (event->mask & IN_CREATE) {
printf("File created: %s\n", event->name);
}
if (event->mask & IN_DELETE) {
printf("File deleted: %s\n", event->name);
}
// 可以添加更多的事件处理
// 假设 inotifytools_next_event 分配了事件结构,这里可能需要释放
// 如果 inotifytools 提供了释放事件的函数,例如 inotifytools_free_event
// inotifytools_free_event(event);
}
// 移除监视并清理 inotify
inotifytools_remove_watch_by_wd(wd);
inotifytools_cleanup();
return 0;
}
Comments | NOTHING